Direct Material Price Variance Calculator
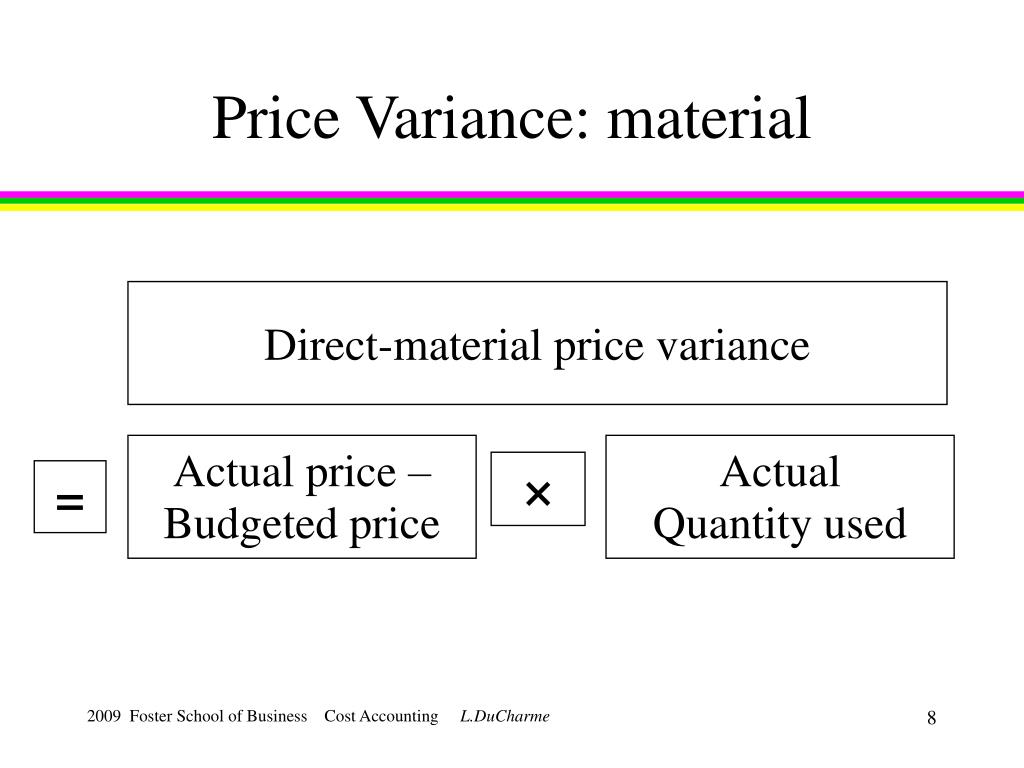
In addition, recognizing the price variance when materials are purchased allows the company to carry its raw materials in the inventory accounts at standard cost, which greatly simplifies bookkeeping. The material price variance calculation tells managers how much money was spent or saved, but it doesn’t tell them why the variance happened. One common reason for unfavorable price variances is a price change from the vendor. Companies typically try to lock in a standard price per unit for raw materials, but sometimes suppliers raise prices due to inflation, a shortage or increasing business costs. The standard cost of actual quantity purchased is calculated by multiplying the standard price with the actual quantity. This amount will represent the expected expenditure on direct material for this many units.
Direct Materials Price Variance
- Market conditions, geopolitical events, and changes in supply and demand can all cause fluctuations in material costs.
- In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured.
- The standard length of timber allowed to manufacture an office chair is 2.75 feet and the standard rate per foot of timber is $3.50.
- The direct materials quantity variance is one of the main standard costing variances, and results from the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity of material used by a business during production.
- This reserve has the effect of adjusting the company’s inventory balances to “actual,” which is appropriate under GAAP.
If there wasn’t enough supply available of the necessary raw materials, the company purchasing agent may have been forced to buy a more expensive alternative. If the company bought a smaller quantity of raw materials, they may not have qualified for favorable bulk pricing rates. In other words, if the business has consumed fewer materials to produce a given level of output than expected, the material quantity variance is said to be favorable. The material quantity variance in this example is favorable because the company manufactured the output using a lesser quantity of materials than what was planned in the budget. Direct materials quantity variance is also known as direct material usage or volume variance.

Our Team Will Connect You With a Vetted, Trusted Professional
An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, indicates that the amount of materials used exceeds the standard requirement. Internal factors, such as production efficiency and waste management, significantly affect material quantity variance. Inefficient production processes, outdated machinery, or inadequate employee training can result in higher material consumption than planned. Implementing lean manufacturing techniques, investing in modern equipment, and providing ongoing training for employees can enhance production efficiency and reduce material waste. Additionally, regular audits of the production process can identify areas for improvement and help maintain optimal material usage.
How do you find the direct materials price variance?
This formula is critical for understanding how actual spending tracks against estimations. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
The ultimate motive behind their calculation is to control costs and enhance improvement. The direct material quantity variance will be adverse if the actual quantity of fabric used in manufacturing 10,000 units of shirts is 30,000 meters and the standard amount of fabric allowed for a single shirt is 2.8 meters. A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials.
Direct Material Quantity Variance FAQs
The material quantity variance can yield unusual results, since it is based on a standard unit quantity that may not be even close to actual usage. The material quantity is usually set by the engineering department, and is based on an expected amount of material that should theoretically be used in the production process, along with an allowance for a reasonable amount of scrap. If the standard is excessively generous, there will be a long series of favorable material quantity variances, even though the production staff may not be doing an especially good job.
The difference between the two postings is the variance of -800, which is posted to the direct materials variance account as a debit representing the unfavorable variance. The difference in the quantity is multiplied by the standard price to determine that there was a $1,200 favorable direct materials quantity using ‘itsdeductible’ to figure the value of donations variance. The net direct materials cost variance is still $1,320 (unfavorable), but this additional analysis shows how the quantity and price differences contributed to the overall variance. Because the company uses 30,000 pounds of paper rather than the 28,000-pound standard, it loses an additional $20,700.
How much is the direct materials quantity variance of Prime Furniture Inc. for the month of December 2022? To begin with, calculating direct material variance involves comparing the standard cost of materials to the actual cost incurred. This comparison helps businesses understand whether they are spending more or less than anticipated on raw materials. The standard cost is typically derived from historical data, industry benchmarks, or predetermined budgets, while the actual cost is recorded during the production process. The variance is calculated using the direct materials quantity variance formula, which takes the difference between the standard quantity and the actual quantity, and multiplies this by the standard price per unit of material. This is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of the direct materials purchased, multiplied by the standard number of units expected to be used in the production process.

